Interactions between the extratropical ocean and the atmosphere on seasonal to multidecadal time scales
by Claude Frankignoul
Claude Frankignoul current research interest includes understanding the interactions between the extratropical ocean and the atmosphere on seasonal to multidecadal time scales.
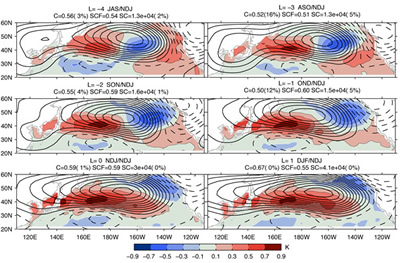
Particular attention has been given to detecting the influence of midlatitude SST anomalies on the atmosphere. Czaja and Frankignoul (1999, 2002, see also Frankignoul and Kestenare 2005) showed that a midlatitude horseshoe SST anomaly pattern has a significant influence on the North Atlantic Oscillation in early winter.Recently, an influence of North Pacific SST anomalies on the atmospheric circulation was found in late summer and early winter (see figure below) in Frankignoul and Sennéchael (2007).
The feedback between SST anomalies and the surface heat flux has been studied in observations and coupled models (e.g. Frankignoul et al. 2004).
The link between the Gulf Stream variability and the atmosphere has been studied using observations (Frankignoul et al. 2001) and ocean GCM simulations (de Coëtlogon et al 2006). The relation with the changes of the North Atlantic circulation are being investigated in a recent hindcast with a higher resolution ocean model.